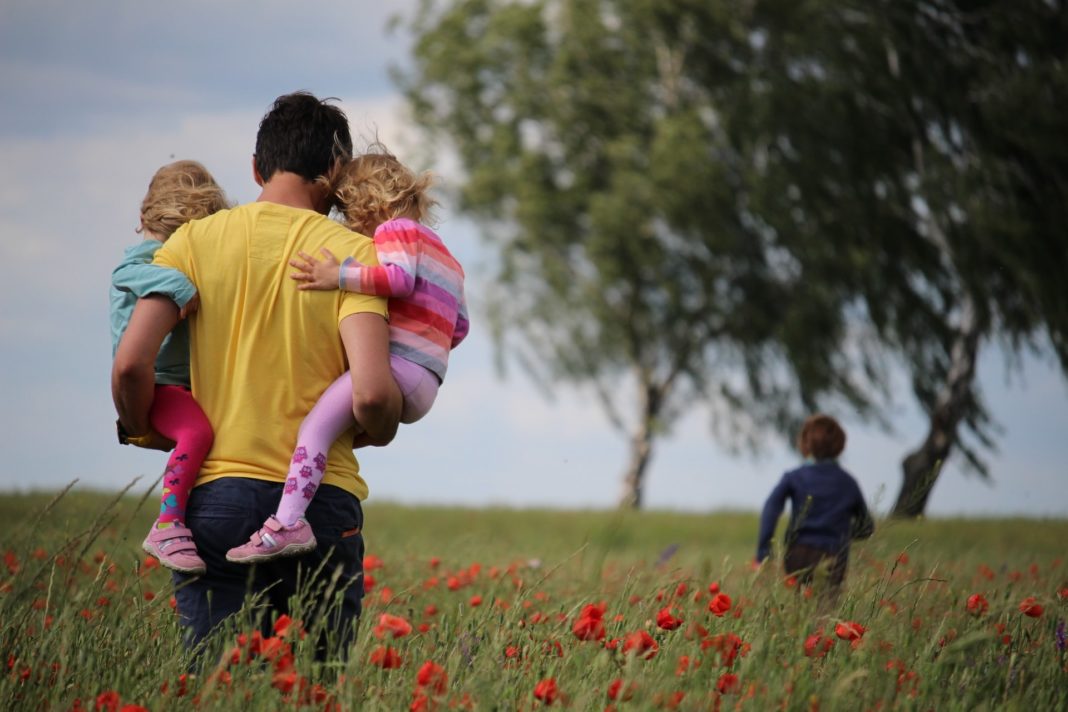
Anxiety disorders are common in children and adolescents, affecting about one-third of teenagers. Anxiety disorder can be a debilitating condition that leads to social withdrawal, depression, and other mental health problems.
Children with anxious/avoidant relationships with parents may produce children who, when they reach adulthood, experience anxiety disorders at higher rates than those from non-anxious families.

This blog post will explore how these childhood development patterns affect the parent-child relationship as well as the adult child’s life in adolescence and adulthood.
How Childhood Development Patterns Affect the Parent-Child Relationship:
Children from anxious families may experience a sense of rejection, abandonment or neglect by their parents. These children are at risk for developing insecure attachments with an avoidant attachment style as well as low self-esteem and high rates of depression when they reach adulthood.
The Adult Child’s Life in Adulthood:
When these childhood development patterns continue into adult life, __ can lead to higher levels of anxiety and social withdrawal than those who experienced more secure relationships with their parents during adolescence.
In order to combat this pattern, it is important that adults use therapy techniques such as mindfulness meditation and progressive muscle relaxation exercises to reduce stress and strengthen coping skills. This will help them transition through difficult periods.